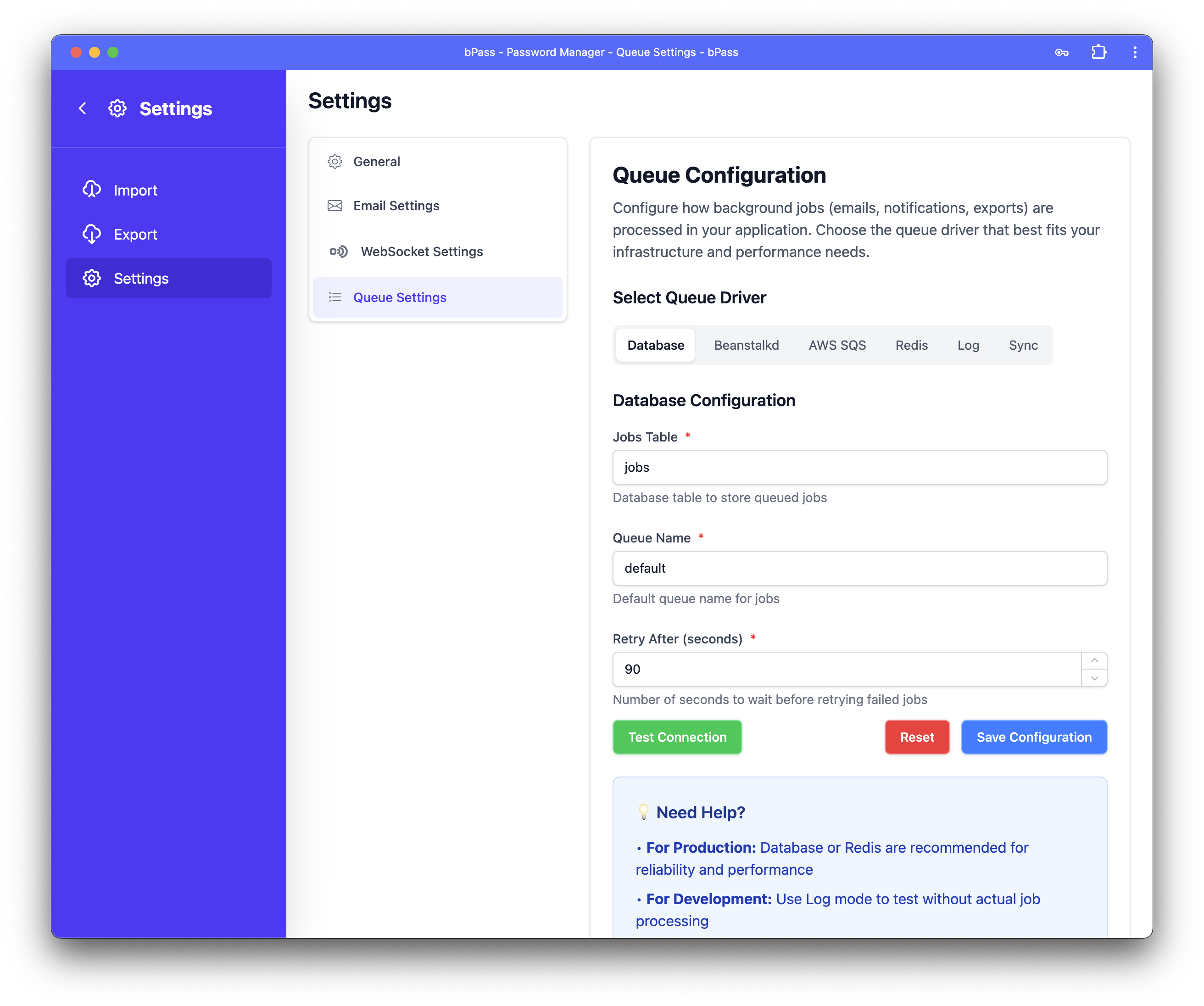
Queue Settings
Configure background job processing for bPass to handle emails, notifications, data exports, and other time-intensive tasks efficiently. Choose the queue driver that best fits your infrastructure and performance requirements.
Overview
Queue processing is essential for: - Email Delivery - Send emails in the background without slowing down user requests - Data Exports - Process large password exports without timeouts - Notifications - Handle user notifications and system alerts - File Operations - Process file uploads, imports, and backups - System Maintenance - Run cleanup tasks and scheduled operations
Queue Driver Options
Database Queue (Recommended for Most Users)
Stores queued jobs in your application database for reliable job processing.
Configuration Settings
- Jobs Table - Database table to store queued jobs (default:
jobs) - Queue Name - Default queue name for jobs (default:
default) - Retry After - Seconds to wait before retrying failed jobs (default:
90)
✅ Advantages
- Reliable and Persistent - Jobs survive server restarts
- Easy Monitoring - View jobs using database tools
- Built-in Retry Mechanism - Automatic retry for failed jobs
- No Additional Infrastructure - Uses your existing database
❌ Disadvantages
- Database Overhead - Additional load on your database
- Worker Process Required - Needs background worker processes
- Single Point of Failure - Database issues affect job processing
Setup Requirements
Requires running worker processes using one of these methods:
Manual Worker (Development)
Supervisor (Production - Recommended)
[program:bpass-worker]
process_name=%(program_name)s_%(process_num)02d
command=php /path/to/bpass/artisan queue:work --sleep=3 --tries=3
autostart=true
autorestart=true
user=www-data
numprocs=4
redirect_stderr=true
stdout_logfile=/var/log/bpass-worker.log
Beanstalkd Queue (High Performance)
A simple, fast work queue designed for distributed systems.
Configuration Settings
- Beanstalkd Host - Server hostname or IP address (default:
localhost) - Queue Name - Beanstalkd tube name for jobs (default:
default) - Retry After - Seconds to wait before retrying failed jobs (default:
90)
✅ Advantages
- Very Fast and Lightweight - Excellent performance
- Built-in Job Priorities - Support for job prioritization
- Low Memory Footprint - Minimal resource usage
- Job Scheduling - Built-in delayed job support
❌ Disadvantages
- Additional Infrastructure - Requires separate Beanstalkd server
- Less Persistent - Jobs lost if Beanstalkd restarts without persistence
- Server Management - Need to maintain Beanstalkd server
Setup Requirements
Install Beanstalkd
# Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt install beanstalkd
# CentOS/RHEL
sudo yum install beanstalkd
# macOS
brew install beanstalkd
Start Beanstalkd Service
AWS SQS Queue (Cloud Native)
Amazon Simple Queue Service - a fully managed message queuing service.
Configuration Settings
- AWS Access Key ID - Found in your AWS IAM console
- AWS Secret Access Key - Found in your AWS IAM console
- AWS Region - Region where your SQS queue is located (e.g.,
us-east-1) - SQS Queue Name - Name of your SQS queue (default:
default) - SQS Prefix - Queue URL prefix (optional)
✅ Advantages
- Fully Managed - No server maintenance required
- Highly Scalable - Automatic scaling based on demand
- Built-in Redundancy - Multiple availability zones
- Pay-per-Use - Only pay for messages processed
❌ Disadvantages
- AWS Dependency - Requires AWS account and credentials
- Network Latency - Internet connectivity required
- Additional Costs - AWS charges for messages and API calls
- External Dependency - Reliant on AWS service availability
Setup Requirements
- Create AWS Account and set up IAM user with SQS permissions
- Create SQS Queue in AWS Console
- Generate Access Keys with appropriate permissions:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"sqs:SendMessage",
"sqs:ReceiveMessage",
"sqs:DeleteMessage",
"sqs:GetQueueAttributes"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:sqs:*:*:your-queue-name"
}
]
}
Redis Queue (High Performance)
In-memory data structure store used as a fast message broker.
Configuration Settings
- Redis Queue Name - Queue name for jobs (default:
default) - Retry After - Seconds to wait before retrying failed jobs (default:
90)
✅ Advantages
- Extremely Fast - In-memory processing for maximum speed
- Rich Data Structures - Advanced queue features
- Pub/Sub Capabilities - Real-time messaging support
- Great for Real-time - Perfect for time-sensitive operations
❌ Disadvantages
- In-Memory Storage - Risk of data loss during restarts
- Memory Limitations - Limited by available RAM
- Server Management - Requires Redis server maintenance
Setup Requirements
Install Redis
# Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt install redis-server
# CentOS/RHEL
sudo yum install redis
# macOS
brew install redis
Configure Redis (redis.conf)
# Enable persistence (optional but recommended)
save 900 1
save 300 10
save 60 10000
# Set memory policy
maxmemory-policy allkeys-lru
Log Queue (Development Only)
Logs job information without actually processing them - perfect for development and testing.
✅ Advantages
- No Setup Required - Works immediately
- Useful for Debugging - See all job events in logs
- No Performance Impact - Zero processing overhead
- Safe for Development - Won't send real emails or notifications
❌ Disadvantages
- Jobs Never Execute - No actual processing happens
- No Email Delivery - Users won't receive emails
- No Real Functionality - Only for testing and debugging
⚠️ Development Mode Warning:
- No emails will be sent to users
- No notifications will be processed
- Export operations will be logged but not executed
- All job information appears in application logs
Sync Queue (Immediate Processing)
Executes jobs immediately during the web request without queuing.
✅ Advantages
- No Background Workers - No additional processes needed
- Immediate Execution - Jobs run instantly
- Simple Setup - No configuration required
❌ Disadvantages
- Slower Response Times - Users wait for jobs to complete
- Risk of Timeouts - Long jobs can cause request timeouts
- Poor User Experience - Delays in page loading
- Server Blocking - Heavy jobs block other requests
⚠️ Sync Queue Warning: - All jobs execute during web requests - Users must wait for emails and notifications to be sent - Risk of timeouts for heavy operations - Suitable only for development or very light workloads
Configuration Process
Step 1: Select Queue Driver
Use the driver selection slider to choose your preferred queue system.
Step 2: Configure Settings
Fill in the required configuration fields for your chosen driver.
Step 3: Test Connection (if applicable)
For drivers with configuration settings: 1. Click "Test Connection" to verify your settings 2. Watch for status indicators: - 🔵 Testing... - Connection test in progress - 🟢 Connection successful! - Settings are correct - 🔴 Connection failed - Check configuration and try again
Step 4: Save Configuration
Click "Save Configuration" to apply your settings.
Step 5: Start Workers (if required)
For Database, Beanstalkd, Redis, and SQS queues, ensure worker processes are running.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Queue Monitoring
Monitor your queue performance with these commands:
# View queue status
php artisan queue:monitor
# Check failed jobs
php artisan queue:failed
# Retry failed jobs
php artisan queue:retry all
# Clear all jobs
php artisan queue:clear
Log Monitoring
Check application logs for queue-related events:
# View recent queue logs
tail -f storage/logs/laravel.log | grep queue
# Monitor failed jobs
tail -f storage/logs/laravel.log | grep "Failed"
Performance Recommendations
For Production Environments
- Database - Reliable choice for most applications
- Redis - Best performance for high-volume applications
- AWS SQS - Excellent for cloud-native deployments
- Beanstalkd - Great performance with minimal resource usage
For Development
- Log - Perfect for testing without side effects
- Sync - Simple setup for basic development
- Database - Good for testing production-like behavior
For High Traffic
- Redis - Maximum performance for job processing
- Beanstalkd - Excellent performance with job priorities
- AWS SQS - Managed scalability for cloud applications
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Worker Process Not Running
# Check if workers are running
ps aux | grep "queue:work"
# Start worker manually
php artisan queue:work --daemon
Failed Jobs Accumulating
# View failed jobs
php artisan queue:failed
# Retry specific job
php artisan queue:retry 5
# Retry all failed jobs
php artisan queue:retry all
Queue Connection Errors - Verify connection settings are correct - Check network connectivity to external services - Ensure required services (Redis, Beanstalkd) are running - Review application logs for specific error messages
Getting Help
- Check Worker Logs - Review worker process output for errors
- Monitor Queue Status - Use built-in monitoring commands
- Test Connections - Use the connection test feature
- Review Documentation - Check your queue driver's specific documentation
Next Steps: After configuring queues, set up email delivery and websocket connectivity for a complete communication system.